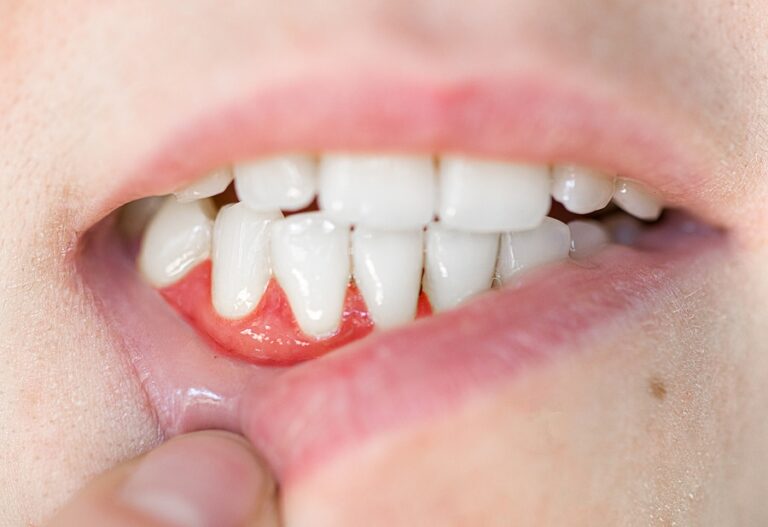
Healing time for cut gums varies based on the severity of the injury and individual care. Minor cuts, like those from accidental biting or aggressive brushing, typically heal within a few days to a week. Proper oral hygiene, including gentle rinsing with saltwater or mouthwash, aids in preventing infection and expedites healing. Health conditions like diabetes can slow down the healing process.
To facilitate healing, it’s essential to avoid irritating the injured gum by steering clear of spicy or acidic foods, tobacco, and alcohol. Seeking dental care for severe cuts is advisable as dentists may offer specific treatments for faster healing and to prevent complications. Persistent pain, excessive bleeding, signs of infection, or delayed healing should prompt consulting a dentist or healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
How do different factors impact gum healing time?
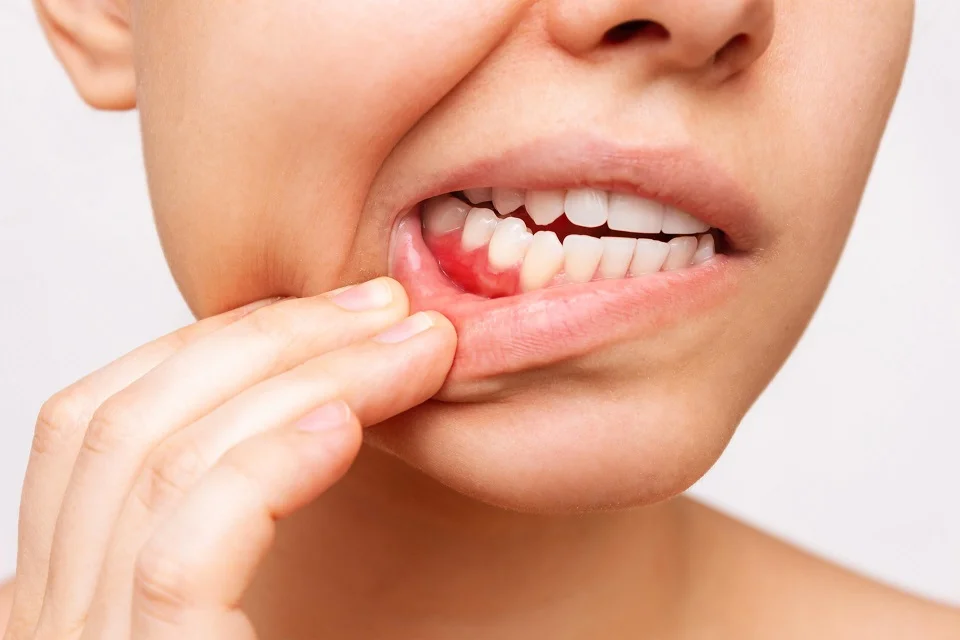
Gum healing time after injury, surgery, or trauma is influenced by several crucial factors. The severity of the damage to the gum tissue is a primary determinant, with minor injuries often healing faster than more extensive ones.
A person’s overall health and immune system also play a vital role—those with compromised immunity or certain medical conditions may experience slower healing. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene through proper brushing, flossing, and using antiseptic mouthwash is essential to prevent infection and promote faster healing.
Smoking can significantly delay gum healing by restricting blood flow, while medications like blood thinners can impact blood clotting and circulation, affecting healing. A balanced diet rich in nutrients, especially vitamin C, is crucial, as nutrient deficiencies can slow down the healing process.
High stress levels, certain underlying health conditions like diabetes, and adherence to post-operative care instructions also influence gum healing times. Individuals vary in their body’s response to healing, so consulting a dentist or healthcare professional for specific guidance and concerns is advisable.
What is the timeline and process for gum healing?
The timeline and process for gum healing can vary depending on the extent of the injury, surgery, or trauma. However, here’s a general overview of the stages and timeline involved in gum healing.
Initial Phase (First 24-48 Hours)
Immediately after an injury or surgery, the body initiates the healing process. Blood clotting occurs to stop bleeding, forming a protective barrier over the wound. This initial clot is crucial in preventing excessive bleeding and protecting the site from infection.
Inflammatory Phase (2-3 Days)
Inflammation sets in, characterized by redness, swelling, and some discomfort. White blood cells rush to the site to fight off potential infections and remove damaged tissue.
Proliferative Phase (Several Days to Weeks)
During this phase, new tissue begins to form. Granulation tissue, composed of blood vessels, collagen, and other cells, fills the wound. This tissue acts as a scaffold for the formation of new gum tissue. Epithelial cells start covering the wound to create a protective layer.
Maturation Phase (Weeks to Months)
The newly formed tissue matures and strengthens. Collagen fibers reorganize, and the wound gradually contracts. The gum tissue continues to heal, becoming stronger and more resilient over time.
Factors like the size and severity of the injury, the individual’s overall health, oral hygiene practices, and lifestyle habits (such as smoking) can influence the duration of each phase and overall healing time.
How to recognize complications during gum healing?

Recognizing complications during gum healing is crucial to ensure proper treatment and prevent further issues. Here are some signs that may indicate complications during the gum healing process:
Excessive Swelling
While some swelling is normal during the initial stages of healing, excessive or increasing swelling beyond the first few days could indicate an issue. Swelling that persists or worsens over time may suggest infection or inadequate healing.
Severe Pain or Discomfort
Mild discomfort or pain is common during the early stages of healing. However, severe or increasing pain that doesn’t subside with time could signal an infection or other complications.
Prolonged Bleeding
Bleeding is expected immediately after an injury or surgery, but it should gradually decrease and stop within a reasonable timeframe. Prolonged or excessive bleeding could indicate a problem with clotting or other issues.
Pus or Discharge
Any discharge, especially if it’s yellow, green, or foul-smelling, may suggest an infection. Pus around the gum area or coming from the surgical site is a sign that requires immediate attention.
Fever or Chills
A fever or chills might indicate an infection spreading beyond the healing site. Elevated body temperature coupled with other symptoms should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional.
Delayed Healing
If there’s a lack of progress in the healing process beyond the expected timeline or if the wound seems to be getting worse instead of better, it could indicate complications.
Redness or Heat
Increased redness or warmth around the gum area might indicate inflammation or infection.
Difficulty Eating or Speaking
If there’s persistent difficulty in eating or speaking due to discomfort or pain at the healing site, it could suggest a problem that needs attention.
FAQ’s
How do you restore cut gums?
Restoring cut gums involves maintaining proper oral hygiene, avoiding irritating substances, and seeking dental care for severe cuts, which may require specific treatments for faster healing.
Do gums grow back if cut?
Gums have limited regenerative capabilities, so while they can heal, they may not grow back fully to their original state after a significant cut or injury.
Do gums fully heal?
Yes, gums have the ability to heal, but the extent of the healing may vary based on the severity of the injury or cut. Complete restoration to their original state might not always occur.
Do mouth gums heal fast?
The healing speed of gums can vary based on several factors, such as the extent of the injury, individual health, oral hygiene practices, and the presence of any underlying health conditions. Minor injuries may heal relatively quickly, while more significant trauma may take longer.
What does an infected gum look like?
Signs of an infected gum may include redness, swelling, tenderness, pus or discharge, bleeding, bad taste in the mouth, and possibly fever. Consulting a dentist is crucial if infection is suspected.
What happens if my gum is cut?
When gums are cut, the healing process begins with blood clotting to stop bleeding, followed by stages involving inflammation, tissue formation, and maturation. Complications like infection or delayed healing may occur and require professional attention.
Final Words
In summary, the healing time for cut gums can vary depending on the injury’s severity and individual care. Minor cuts usually heal within a few days to a week, while proper oral hygiene practices, such as gentle rinsing with saltwater or mouthwash, aid in preventing infection and expediting healing. Health conditions like diabetes can slow down the process.
To facilitate healing, avoiding irritating factors like spicy foods, tobacco, and alcohol is essential. Seeking dental care for severe cuts is advisable as dentists may offer specific treatments for faster healing and to prevent complications.