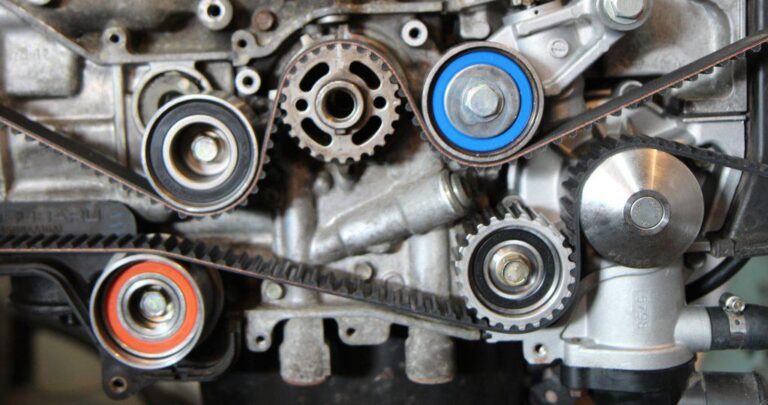
The “Drive Belt vs Timing Belt” comparison revolves around their roles in a vehicle’s engine. A drive belt powers accessories like the alternator and power steering, ensuring they function correctly. It’s cost-effective, simple, but requires regular inspection for wear.
On the other hand, a timing belt synchronizes the engine’s crankshaft and camshaft, precisely timing valve openings. While it offers accurate engine performance, a failing timing belt can lead to severe engine damage. Both have advantages – drive belts for simplicity, and timing belts for precision
Drive Belt
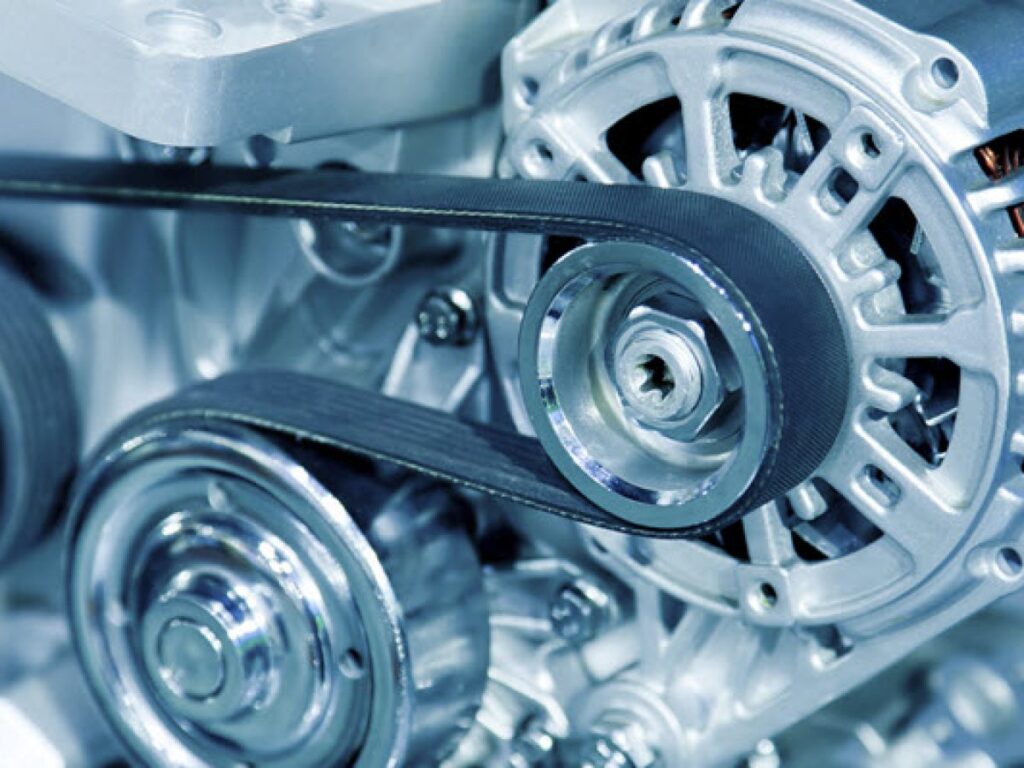

A drive belt, also known as a serpentine or accessory belt, is a flexible loop of rubber or synthetic material that connects various engine components to ensure their synchronized operation.
The primary purpose of a drive belt is to transfer power from the engine to multiple components, such as the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor. It plays a vital role in driving these accessories and ensuring the overall functionality of the vehicle.
Types of Drive Belts
Serpentine Belts: Modern vehicles often use a single serpentine belt that winds through multiple pulleys, driving various engine components.
V-Belts: Older vehicles might have multiple V-belts, each dedicated to a specific accessory.
Functions in a Vehicle
Power Transmission: The drive belt transfers mechanical power from the engine’s crankshaft to different accessories, enabling their operation.
Accessory Operation: It drives components like the alternator, which generates electrical power, the water pump for engine cooling, the power steering pump for assisted steering, and the air conditioning compressor for climate control.
Synchronization: The drive belt synchronizes the movement of these accessories, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in the vehicle’s various systems.
Timing Belt
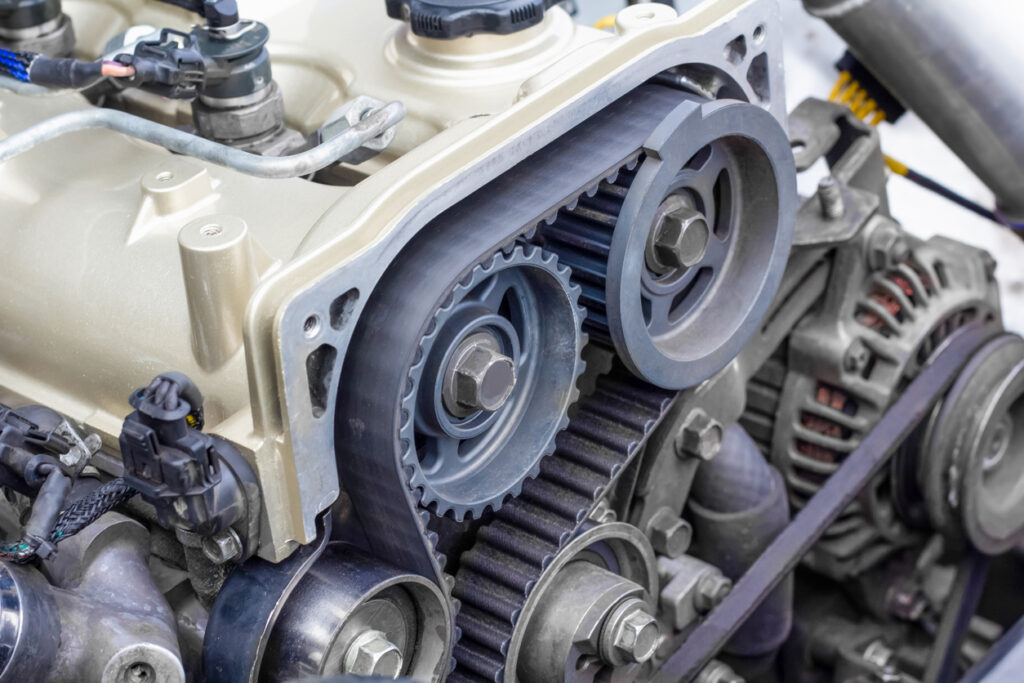
A timing belt is a toothed, reinforced rubber belt that connects the crankshaft and camshaft(s) in an internal combustion engine. Its purpose is to synchronize the rotation of the engine’s crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring precise timing of the opening and closing of engine valves.
The timing belt plays a critical role in controlling the timing of the engine’s valve operation, allowing for the precise intake of air and fuel and the expulsion of exhaust gases.
Distinctive Features from Drive Belts
Unlike the smooth, continuous design of drive belts, timing belts have teeth or cogs that mesh with the gears on the crankshaft and camshaft. This toothed design ensures accurate and synchronized movement.
Timing belts are often housed within a protective cover or casing to prevent debris or contaminants from affecting their performance. This enclosed design distinguishes them from the exposed nature of some drive belts.
Importance in Engine Synchronization
The timing belt precisely controls the opening and closing of the engine valves, determining when air and fuel enter the combustion chamber and when exhaust gases are expelled.
Proper synchronization prevents the pistons and valves from colliding, avoiding potential catastrophic engine damage. Engine timing is crucial for efficient combustion and overall engine performance.
Key Differences Between Drive Belt and Timing Belt
Construction and Materials
Drive belts are typically made of rubber or a rubber-like material, often reinforced with fibers like polyester or nylon. They have a smooth, flexible design.
Timing belts have a toothed design with cogs or teeth made from durable materials such as rubber, fiberglass, or aramid fiber. This toothed construction enhances grip and precision.
Functions Within the Vehicle
Drive belts primarily transmit mechanical power from the engine’s crankshaft to various accessories like the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor. They ensure the proper operation of these components.
Timing belts synchronize the movement of the engine’s crankshaft and camshaft(s). They control the timing of the opening and closing of engine valves, crucial for combustion and overall engine performance.
Impact on Engine Performance
The failure of a drive belt can lead to the malfunctioning of accessories it drives, affecting functions like charging, steering, and cooling. While critical, a drive belt failure doesn’t typically result in catastrophic engine damage.
The timing belt is integral to engine operation, and its failure can lead to serious consequences. If the timing belt breaks or slips, the engine’s pistons and valves may collide, causing significant damage and potentially rendering the engine inoperable.
What are the advantages and considerations for drive belts?
Advantages of Drive Belts
Simplicity: Drive belts are simple in design, consisting of a continuous loop of material. This simplicity makes them easy to manufacture and replace.
Cost-Effective: Compared to timing belts or chains, drive belts are often more cost-effective both in terms of manufacturing and replacement. This cost advantage is beneficial for vehicle owners.
Ease of Installation: Installing drive belts is generally straightforward, making it a less complex process for mechanics and DIY enthusiasts alike.
Considerations and Limitations of Drive Belts
Wear and Tear: Drive belts are subject to wear and tear due to continuous movement and exposure to environmental factors. Over time, they can develop cracks, fraying, or other signs of deterioration.
Limited Lifespan: The lifespan of a drive belt is typically shorter compared to timing belts. As a result, they may require more frequent replacement to prevent unexpected failures.
Regular Maintenance: Periodic inspection is crucial to identify signs of wear early on. Visual checks and regular maintenance help prevent sudden belt failures and ensure the consistent functioning of accessory components.
What are the pros and cons of timing belts?
Pros of Timing Belts
Precise Engine Timing: Timing belts play a crucial role in synchronizing the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft(s), ensuring precise timing of valve opening and closing. This precision contributes to efficient engine performance.
Quieter Operation: Timing belts generally operate more quietly than chains, providing a smoother and quieter driving experience.
Lighter Weight: Timing belts are lighter than timing chains, contributing to overall weight reduction in the engine.
Cons and Considerations of Timing Belts
Limited Lifespan: Timing belts have a finite lifespan and are prone to wear and aging. They require regular replacement to avoid the risk of sudden failure.
Potential for Serious Engine Damage: If a timing belt fails, it can lead to serious consequences, including interference between pistons and valves. This can result in significant engine damage and potentially render the engine inoperable.
Maintenance Costs: While timing belts themselves are often less expensive than timing chains, the cost of labor for replacement can be higher. Replacement is a complex process, and the entire timing belt system may need to be replaced.
Inconvenient Failure: Unlike drive belts that may affect accessory components, a timing belt failure can cause a sudden and complete breakdown of the engine, necessitating towing and extensive repairs.
When should drive and timing belts be replaced?
The replacement intervals for drive belts and timing belts vary depending on the vehicle make and model. However, here are general guidelines
Drive Belts:
Visual Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the drive belt regularly for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or glazing.
Manufacturer Recommendations: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for replacement intervals, which are typically specified in the vehicle’s maintenance schedule. This can range from 40,000 to 100,000 miles or more.
Timing Belts
Manufacturer Recommendations: Timing belts have a specific lifespan recommended by the manufacturer, typically expressed in terms of mileage or time (e.g., every 60,000 miles or every 5 years). Consult the vehicle’s manual for precise information.
Visual Inspection: Unlike drive belts, timing belts are more challenging to visually inspect due to their enclosed nature. Therefore, adherence to replacement intervals is crucial.
It’s important to note that ignoring the recommended replacement intervals can lead to belt failure, which may cause extensive engine damage. If there are signs of wear or if the vehicle has reached the recommended replacement mileage, it’s advisable to replace the belts promptly.
Additionally, some vehicles may use timing chains instead of belts, and these typically have a longer lifespan and may not require regular replacement.
FAQ
Is timing belt and engine belt the same?
No, a timing belt and an engine belt are not the same. While an engine belt is a broad term that can refer to various belts in the engine, a timing belt specifically controls the timing of the engine’s valves.
When should a drive belt be replaced?
The replacement of a drive belt depends on factors like wear and tear. Regular inspections are crucial, and replacement is recommended when signs of damage, such as cracks or fraying, are observed.
Is the timing chain the same as the drive belt?
No, a timing chain is not the same as a drive belt. The timing chain is a metal chain, while a drive belt is typically made of rubber or similar materials.
What is another name for the timing belt?
Another name for the timing belt is a cam belt. Both terms refer to the same component responsible for synchronizing the engine’s crankshaft and camshaft.
How long do timing belts last?
The lifespan of a timing belt varies, but it is generally recommended to be replaced every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
Can a timing belt last 10 years?
While the mileage is a more common measure, a timing belt’s lifespan can also be influenced by time. It is advisable to replace a timing belt every 5 to 10 years, even if the mileage is within the recommended range.
Does timing belt change speed?
No, the timing belt’s primary function is to synchronize the timing of the engine’s valves, ensuring they open and close at the right moments. It does not directly affect the speed of the vehicle.
Can a timing belt last 200,000 miles?
While some timing belts may last up to 200,000 miles, it’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations. Regular inspections and adherence to replacement intervals are essential to prevent unexpected failures.
Final thoughts
To sum it up, knowing the difference between a drive belt and a timing belt is like understanding the jobs of helpers in a car. The drive belt helps with simple tasks for things to work smoothly, and the timing belt is super important to make sure all the engine parts work together at the right time.
Both are essential, so it’s important to regularly check and change them to keep the car happy. Whether it’s the helper or the boss, taking care of these belts means the car will run well and won’t have unexpected problems. Always remember, a little attention to these belts keeps the car in good shape. Drive safely!

